Recently, a joint team of the Institute of Physics and Chemistry Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Tsinghua University, led by Researcher Liu Jing, reported a 3D printing technology for in vivo implantable biomedical electronic devices based on liquid metals. The research article was published in the "Science Report" series of Nature Publishing Group journals.
In this study, the researchers first proposed a method for in-vivo manufacturing of medical electronic devices by inkjet injection molding directly at the target tissue in the body in a minimally invasive manner. First, the biocompatible packaging material was injected into the body to solidify Specific structure, in this area, conductive metal ink, insulating ink and matching micro / nano scale devices are sequentially injected to form the target electronic device. By controlling the direction of injection of the microsyringe, injection site, injection volume, The 3D printing steps such as needle displacement and speed can build a terminal device with a predetermined shape and function at the target tissue. Since all devices and units are implemented using liquid injection based on microneedles, the entire surgical procedure is highly invasive. If the surgical robot is further adopted, this step can be greatly simplified and the degree of automation can be improved. The new method opens up a whole new way for biomedical flexible electronic implantation technology.
Clinically, commonly used implantable medical devices, such as brain pacemakers, cardiac pacemakers, and nerve stimulators, provide indispensable support for the physical function of patients with cerebral stroke, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. But its shortcomings are also very obvious. For example, the implantation process of such devices is cumbersome and invasive, and patients often undergo a series of complex procedures such as craniotomy, thoracotomy, device implantation, and wound suture. On the one hand, it will cause physical and mental pain for patients. Excessive wounds are also prone to surgical complications and infection risks. At the same time, surgery and equipment operation support also invisibly bring economic pressure to patients. Discomfort to the application object. Therefore, the realization of a convenient and quick in-vivo flexible electronic device direct printing manufacturing method will not only relieve the burden of patients, but also contribute to the advancement of smart implantable medical electronic technology.
The Liu Jing group has been committed to promoting the application of room-temperature liquid metal, a new functional material, in the fields of electronic information, energy, medical and health technology, etc. for more than 10 years, and has achieved a number of pioneering results. In 2013, the group published a series of important papers that had a great impact, and was featured in the internationally renowned scientific media MIT Technology Review, Nature Asia, Chemistry World, National Geographic News and other special reports. Yin Hejun, vice president of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Gu Binglin, chairman of the Beijing Association of Science and Technology, and academician Yang Wei, director of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, have made special trips to the laboratory for investigation. This medical electronic bio-in vivo 3D printing molding technology is a breakthrough solution proposed by the laboratory based on long-term accumulation and combined with major needs in clinical medicine, refreshing people's understanding of in-vivo electronic applications and conventional 3D printing technology, resulting in flexible devices With its high compliance, conformability, low invasiveness and low cost characteristics, it shows good application prospects and is of great significance in the field of implantable biomedical electronic technology.
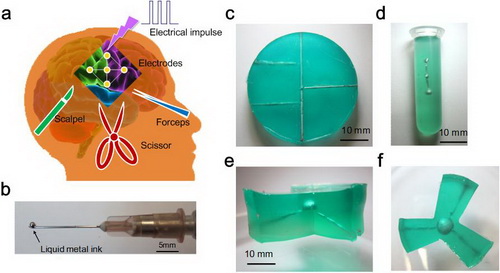
In vivo 3D printing technology of injectable medical devices and the realized space electrodes (as shown in the upper left figure, even if a simple electrode is implanted, traditionally, it often needs to be realized by complex surgical procedures)
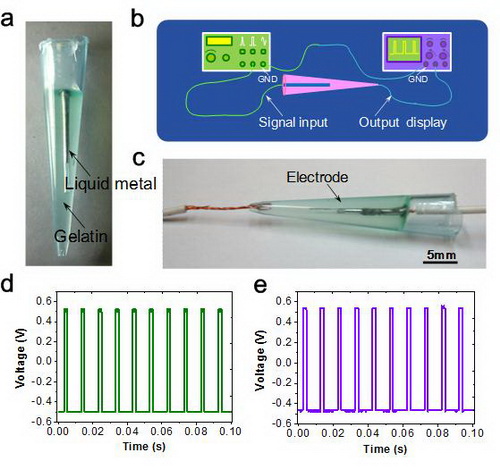
Liquid metal electrode encapsulated in cured transparent medium and its performance test
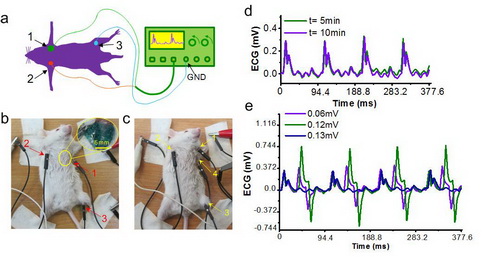
High signal-to-noise ratio measurement and electrical stimulation of mouse ECG signals by means of liquid metal electrodes injected into the body
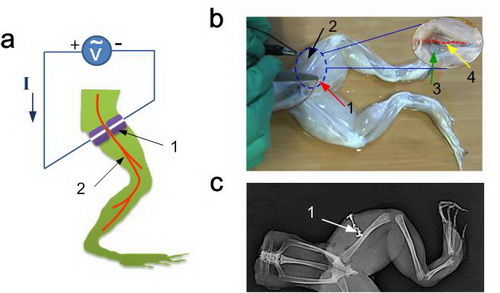
Injection-based liquid metal electrode stimulates sciatic nerve in bullfrog legs
skin analysis machine,Skin Analyzer,Facial Skin Analyzer
Xi'an Double H Health Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.xadoubleh.com