DI is an abbreviation for Direct-Imaging. Compared with off-line plate making CTP, the greatest advantage of on-machine plate making DI is that plate making speed is fast and the preparation time is short before start-up, which is very suitable for short-printing market with short delivery time. Image processing techniques and media systems that do not require post-processing are often used. The advantages of DI over traditional offset printing:
电脑 Computers directly to the press can fully implement standardization and data quality control.
è´¨é‡ Improve the quality of outlets: direct imaging, free printing of printing plates, completely avoiding the loss of outlets, and can completely reproduce 1-99% of outlets on the printing plate. Dots are richer and more continuous; edges are sharp and ink is printed more quickly. Smaller expansion rates, higher print densities, more vivid prints, and more contrast.
â—‡ Digital layout, imposition efficiency has been greatly improved, overprint accuracy has been greatly improved, and human error has been reduced.
â—‡ Based on ICC-based color management, accurately simulate the printer's color space with the specified digital proofing device.
打 Instant proofing, last minute change.
全自动 Automatic printing operation, from automatic plate loading to automatic cleaning.
â—‡ Full digital flow, prepress data directly remotely control ink fountain area presets.
稳定 Stable and reliable, easy to calibrate.
4, digital proofing
Proofing technology is an important part of print reproduction technology. Digital proofing is a proofing technology that converts digital pages directly into color proofs. It does not require any intermediary media such as film and plates, and is an essential supporting technology for CTP and DI. Digital proofing technology is divided into soft proofing and hard proofing. The so-called soft proofing is to look at the color on the screen, the main purpose is to facilitate the trimming process. With the popularity of color management and network technology, digital proofing technology can be used to achieve remote proofing as a means of communicating with customers.
5, digital printing
A laser or light emitting diode is used to etch or electronically image an electronic plate or photoreceptor drum, and digitalized graphic information is printed directly from the computer. An electronic plate or drum allows you to change the image or text of each page while printing.
The advent of digital presses (Digital Press/Printer) has made it possible to convert digital pages directly into printed matter, integrating traditional prepress, printing and even postpress operations into a single unit that is completed by a computer system. This is a "downright" digital production technology, there is no intermediary physical media throughout the entire production process, all products exist in the production system before the meeting with the customer digitally, circulation and processing and processing. Digital printing no longer uses plates in the traditional sense and belongs to Plateless Printing, so the ability to have Variable Information Printing and On-demand Printing will become increasingly The rise of the on-demand/personalized printing market is the main production technology means.
Compared with traditional printing, Andrew Paparozzi of the National Printing Association and the Center for the Study of the Economy of Offset Printing: “Digital printing is sometimes a supplement to traditional printing, and sometimes it is a strong competitor to traditional offset printing.†Traditional printing is “after production The "re-sales" production model, and digital printing is the "sales after production" production model. Therefore, once digital printing is combined with the Internet, it can build a global on-demand production and service system to meet the needs of the gradually developed and personalized printing and publishing market.
The 21st century is a era of knowledge economy with digital information and networking as the main technical features. The printing and publishing industry will become the main provider of information media and become an important part of the information industry.
Second, the development of color reproduction technology
The development of printing technology has gone through different stages. From the time point of view, three-color printing technology and multi-color printing technology emerged in the middle of this century. In the 1970s, the four-color printing process was popularized and applied in China. In the late 1970s, the non-color structure process was born and developed. It has developed rapidly. In the 1990s, high-fidelity (originally true color) printing processes, the printing quality of which was comparable to color photographs, emerged.
The feature of three-color printing is that only the original inks of yellow, magenta, and cyan are used to copy the original. The black in the original is formed by mixing three primary colors of ink according to the principle of neutral gray balance, as shown in FIG. 2a. (See Figure 2.) In terms of color theory, the three-color process is adequately feasible, and the number of overprints is small, which should be more advantageous for printing. However, due to the limitations of materials and technologies, the three-color process has poor results in terms of image contrast and gray balance, and has not been truly promoted.
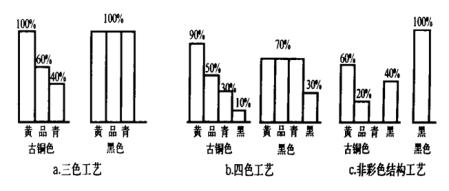
In order to solve the above problems, a black version was added on the basis of the three-color process. Based on the three primary colors, the black version plays the role of skeleton and contour, so the four-color process began to be applied. The addition of the black edition makes the neutral gray balance of the three primary inks easier to control, improves the contrast of the picture, improves the subtle level of dark tone, and reduces the amount of color ink. In theory, however, the addition of the black plate requires the removal of the three primary color components that make up the achromatic color, i.e. the removal of the underlying color. For example, if you want to copy the bronze on the original, if you add 10% black (as shown in Figure 2b), you can remove the same amount of yellow, magenta, and blue primary inks, which can also achieve good color reproduction. Background color removal only acts on the neutral gray area, and due to the limitation of the range of the adjustment, the amount of removal is limited and can only be removed at most 30%-40%, so the black version of the four-color process mainly plays a regulatory role. As the black version is added, a certain color (such as bronze) on the original will be described by the four parameters of yellow, magenta, cyan, and black, but because black is not an independent parameter (black can be matched by yellow, magenta, and blue As a result, the description of color in the four-color process theory still has only three parameters that are independent, conform to the basic principles of colorology, and have been applied and promoted in practice.
With the advent of the digital electronic color separation machine, each pixel on the manuscript can be quantified and the background color can be removed 100%. The color of the image can be reproduced by two of the three primary colors plus black ink (as shown in Figure 2c, the bronze color is represented by yellow, magenta, and black, and the background color equivalent to green is completely removed). The process of adding the black to the original color and forming the image is called an achromatic structure process, which solves the problems that the neutral gray is not stable and the printability is poor during the process of replacing the middle and low speed printing machines with a multi-color high-speed printing machine. The achromatic structure process breaks the traditional practice of color reproduction based only on the three primary colors and highlights the role of the black version. The black version is no longer in a subordinate position. The level and color of the entire picture must be controlled by the black version. As a complete structure, the plate plays an important role in influencing the overall color combination.
The use of long-term black printing can improve the fluctuation of the ink in the multi-color printing process, improve the reliability of color reproduction, and also enhance the printing adaptability. However, the non-color structure process cannot realistically reproduce the bright and pure purple blue, green and orange red, so that the non-color structure printing is limited in the range of copying the original. The GTP process of DTP and CTP technology adopts a long tone black edition, and the removal amount can be controlled flexibly from 0 to 100%. At the same time, color gain is added to increase the contrast and color saturation of printed products.
The color reproduction technology has been greatly developed since it does not use a black version of the three-color printing to use a black version of the four-color printing, but also highlights the role of the black plate in the achromatic structure process.
Our linear actuator widely used for home , office ,robotics, cabinets, home care beds, massage chairs. One of the main advantages of a track actuator is the ability to provide the same travel distance as a standard actuator, without increasing the overall dimension of the device.
It`s easy to Install and integrate with just about any application. In just a few seconds you can adjust the height to your needs. Actuators are ideal solution for your need.

Home Electric Linear Actuator,24V Linear Actuator,Linear Actuator For Solar,Linear Actuator Waterproof,Small Linear Actuator
Suzhou Uplift Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , http://www.uplifting-desk.com