Ion chromatography has played an important role in inorganic anions and cations, organic acids and bases and biological samples. Especially for inorganic anions. It can analyze about 40 kinds of anions in all kinds of samples, playing a role that other analysis methods are difficult to replace.
1. Anion analysis
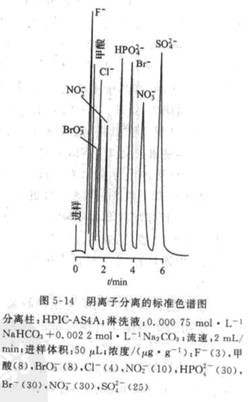
The standard chromatogram of negative ion separation is shown in Figure 5-14. The eluent that suppresses column-type ion chromatography must have two main conditions: First, it can replace the measured ion from the separation to the resin. That is, the ion pair The affinity of the ion exchange resin is close to or slightly greater than the affinity of the side ion pair from the exchange resin. The second is the inhibition reaction. The reaction product is a weak electrolyte or water with low conductivity. The qualified anion eluents are B4O2-, OH-, HCO3-, CO3, glycine, p-cyanophenol, etc. The first four are the most Commonly used. Generally, the monovalent ion eluent is used for the monovalent ion eluent. The divalent ion is used for the divalent ion eluent. In the anion eluent, the HCO3- / CO3-,-solution contains both monovalent eluent ions and divalent eluent ions. It can be used for the separation of a variety of mixed anion samples and is a universal anion eluent. Also known as standard anion eluent. By changing the ratio of HCO3- and CO3-, the pH and selectivity of the eluent can be changed; changing the concentration can change the elution speed of the ion to be measured without changing the elution of the separated ion order. When separating anions by single-column non-suppressed ion chromatography, the eluent usually uses pH 4-9 organic acid salt buffer solution. Commonly used are: stupid formate aqueous solution, suitable for separation of monovalent and divalent anions, the concentration is 0.5X10-^-5X10-3mol.L-1 "; phthalate aqueous solution. Separation ability is better than benzoic acid Strong salt, can be used for separation of divalent anions and strong retained ions. Adjust pH 3-4, and can also be used as an eluent for separation of organic acid mixtures such as acetic acid, formic acid, and long acid; Eluent. The charge is 3, which can be used when analyzing strongly retained ions.
2. Cation analysis
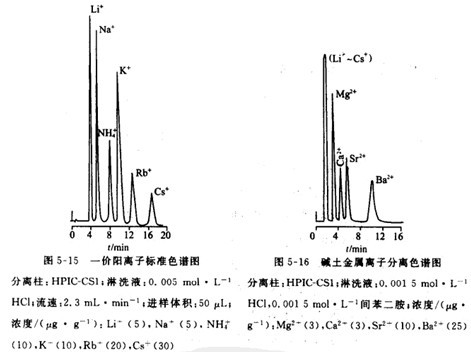
Double-column cation analysis. Usually two kinds of eluent: 0.005mol.L-1'HCI are used to wash monovalent cations. 0.0015mol.L-1HCI and. 0.0015mol.L-1 A mixed solution of phenylenediamine is used to wash alkaline earth metals. The separation effects are shown in Figures 5-15 and 5-16 respectively.
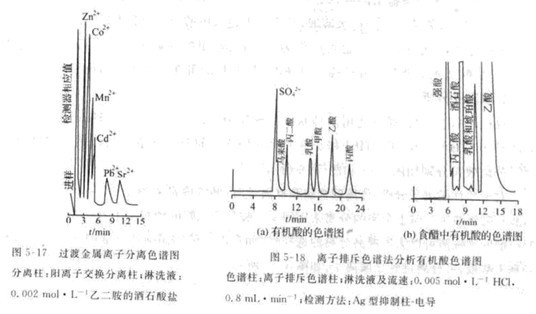
For single column cation analysis. When separating alkali metal and right ion, 0.002mol·L-1 'hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and perchloric acid are often used as eluent. For the separation of alkaline earth metals, the nitrate salt of m-phenylenediamine and ethylenediamine is used as the lotion lotion. The use of a complexing agent-containing eluent can greatly improve the selectivity of separation. For example, adding tartarate or hydroxybutyrate to the nitrate solution of the second limb can separate transition metal ions. As shown in Figure 5-17 .
3. Organic matter analysis
Ion chromatography also has important applications in the analysis of organic acids, nitrogen-based gums, sugars, organic amine compounds, etc. Especially in organic acid analysis. Organic acid ion color increase analysis can use the conventional ion exchange separation mechanism. It can also use the ion rejection separation mechanism. The ion rejection separation is to fill the separation column with a strong acid ion exchange resin. The sulfonic acid group on the resin ionizes out the hydrogen It has a negative charge. It has a repelling effect on the separated organic acid anions. The repulsive force is related to the organic charge, molecular structure and size. The component with the highest repulsion force flows out first. The chromatogram for the separation of organic acids using the ion repulsion mechanism is shown in Figure 5-18:
NINGBO CHEN WEI SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.chenweisupply.com