 The dilatant fluid exhibits an increase in the shear rate and an increase in the viscosity of the fluid. This kind of fluid is very rare in the ink field. Some high solids systems and quicksands are typical dilatant fluids.
The dilatant fluid exhibits an increase in the shear rate and an increase in the viscosity of the fluid. This kind of fluid is very rare in the ink field. Some high solids systems and quicksands are typical dilatant fluids. Clays and organoclays are naturally hydrophilic clays such as montmorillonite and bentonite. When dispersed in water, clay particles begin to swell and separate into platy clay particles. Due to the interaction between the flaky clays, they form a three-dimensional structure as "small houses" in water. Therefore, clay has thickening properties (Fig. 5).

Natural clays can be used in aqueous gravure and relief printing inks to increase the rheological properties of the ink and prevent ink settling.
However, natural clays cannot be dispersed in oily and solvent inks and therefore do not have the effect of rheological agents. In order to thicken oily and solvent-based inks, hydrophilic natural clays need to be modified with various hydrophobic quaternary ammonium salt mixtures.
The reaction of montmorillonite and quaternary ammonium salt is shown in Figure 6.
The reaction process is the exchange of sodium ions between the quaternary ammonium salt particles (CL-) and the clay surface, so that the organic compounds adhere to the clay surface through chemical bonds and the reaction product is organoclay. The resulting low molecular weight salts can be washed off with water (Figure 7).
However, natural clays cannot be dispersed in oily and solvent inks and therefore do not have the effect of rheological agents. In order to thicken oily and solvent-based inks, hydrophilic natural clays need to be modified with various hydrophobic quaternary ammonium salt mixtures.
The reaction of montmorillonite and quaternary ammonium salt is shown in Figure 6.
The reaction process is the exchange of sodium ions between the quaternary ammonium salt particles (CL-) and the clay surface, so that the organic compounds adhere to the clay surface through chemical bonds and the reaction product is organoclay. The resulting low molecular weight salts can be washed off with water (Figure 7).

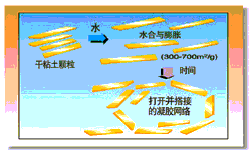
The commercial organoclay powders are present in the form of agglomerates in the form of flake-like deposits and therefore require wetting and mechanical energy to further disperse these flakes. The addition of polar functional group-containing substances, such as low molecular weight alcohols, water, and propylene carbonate, will contribute to the dispersion of clay flakes. The organoclay eventually disperses into a rheologically functional structure (Figure 8).
Currently, the control of the viscosity of the plate ink can be achieved by reactive gels (chemical interactions) and non-reactive gels (physical interactions), or a mixture of two gels. Reactive gels include aluminum salts of fatty acids and their compounds, organic titanates, oxides and hydroxides of Ca, Mg, Zn, and amino acid polymers.
Currently, the control of the viscosity of the plate ink can be achieved by reactive gels (chemical interactions) and non-reactive gels (physical interactions), or a mixture of two gels. Reactive gels include aluminum salts of fatty acids and their compounds, organic titanates, oxides and hydroxides of Ca, Mg, Zn, and amino acid polymers.

(To be continued)
Kid Bicycle,Folding Bicycle,Kid Bicycle
Baby Car Seat High Landscape Car Co., Ltd. , http://www.chbabycarseat.com